Cameroon’s cultural diversity is showcased through various ethnic groups and indigenous languages. The country boasts a rich tapestry of traditions, customs, and languages, making it a fascinating destination for cultural exploration.
With over 250 distinct ethnic groups, each with its unique practices and beliefs, Cameroon offers a diverse and vibrant cultural landscape to discover. From the Fulani in the north to the Baka in the rainforest region, Cameroon’s indigenous populations contribute to the country’s diverse cultural heritage.
In addition to the ethnic groups, Cameroon is home to around 230 different languages, reflecting the linguistic diversity that exists within its borders. This linguistic richness adds to the country’s cultural tapestry, making it a truly unique and captivating destination for those interested in exploring diverse cultures. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of Cameroon’s ethnic groups and indigenous languages to uncover the beauty and complexity of this vibrant nation.
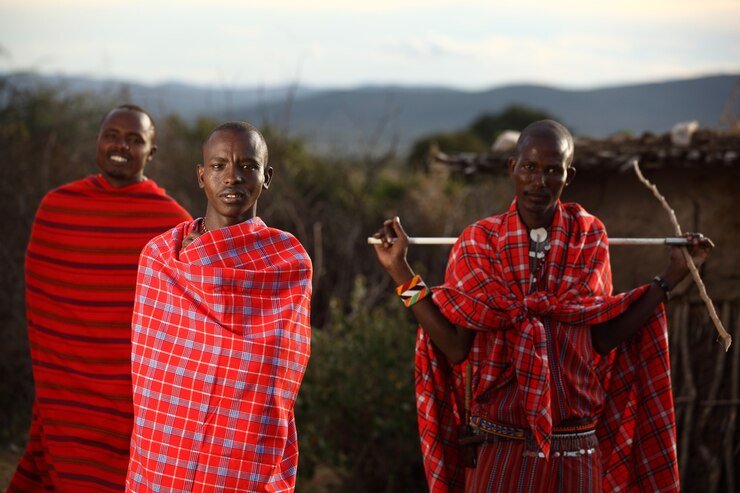

Ethnic Groups In Cameroon
Cameroon’s cultural diversity shines through its rich tapestry of ethnic groups and indigenous languages. Discover the vibrant traditions, customs, and heritage of these communities, adding depth and beauty to the nation’s cultural fabric.
Major ethnic groups
|
Unique characteristics
|
| Major ethnic groups in Cameroon include Bantu, Semi-Bantu, and Sudanese. |
Bantu groups are known for their vibrant traditional dances and colorful attire. |
| Semi-Bantu communities are recognized for their elaborate wood carving skills. |
Sudanese tribes are known for their intricate beadwork and basket weaving. |
Indigenous Languages
Cameroon exhibits a rich tapestry of indigenous languages, with over 250 spoken across the country. Each ethnolinguistic group contributes to this vibrant linguistic landscape. Recognizing the importance of preserving these languages, various initiatives and organizations are dedicated to their documentation and revitalization. Efforts such as language education programs and literacy campaigns aim to ensure the survival of these cultural treasures for future generations to appreciate and safeguard. By celebrating the diversity of indigenous languages, Cameroon fosters a society that cherishes its unique linguistic heritage.
Traditional Practices
Cameroon is renowned for its vibrant cultural diversity, encompassing various ethnic groups and indigenous languages. One significant aspect of this diversity is the prevalence of traditional practices that have been passed down through generations.
Cultural rituals and ceremonies play an essential role in Cameroon’s society. These traditions allow communities to connect with their ancestors, reinforce social cohesion, and celebrate important milestones. Whether it is the elaborate wedding ceremonies or the initiation rites of passage, these customs hold deep significance for the respective ethnic groups.
Moreover, traditional music and dance forms are integral to Cameroon’s cultural heritage. These art forms are not only a means of entertainment but also serve as a form of communication and storytelling. Traditional music instruments, such as the balafon and ndop, are played with great skill and finesse, producing captivating melodies that captivate both young and old.
This rich cultural tapestry sets Cameroon apart, showcasing the country’s commitment to preserving its diverse heritage. By actively engaging in their traditional practices, Cameroonians continue to cherish their ancestral roots and ensure that these invaluable customs are passed on to future generations.

Cultural Heritage Sites
Cameroon’s cultural diversity is a treasure trove of ethnic groups and indigenous languages. The country is home to a variety of cultural heritage sites that showcase its rich history and traditions. These sites are of great significance and are essential for preserving Cameroon’s cultural heritage for future generations.
Some of the prominent cultural heritage sites in Cameroon include the Dja Faunal Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its diverse wildlife and dense rainforests. The Lobeke National Park is another important site that is home to various endangered species.
Another notable cultural site is the Bali-Nyonga Palace, which showcases the traditional architecture of the Bamileke people. The Lamido’s Palace in Foumban is a remarkable example of the historical and cultural significance of the Bamoun people.
The preservation of these cultural heritage sites is crucial to maintain the country’s cultural identity and promote tourism. Efforts are being made to raise awareness about their importance and implement sustainable practices to protect them from degradation or destruction.
Challenges And Opportunities
Cameroon’s cultural diversity presents both challenges and opportunities for the nation. Challenges include potential conflicts arising from cultural differences, as well as the risk of indigenous languages and traditions being marginalized.
On the flip side, there are opportunities to promote and celebrate the rich cultural tapestry of Cameroon. Embracing diversity can lead to greater social cohesion and understanding among ethnic groups. It also offers the chance to preserve and revitalize indigenous languages and traditions, contributing to a vibrant and inclusive national identity.
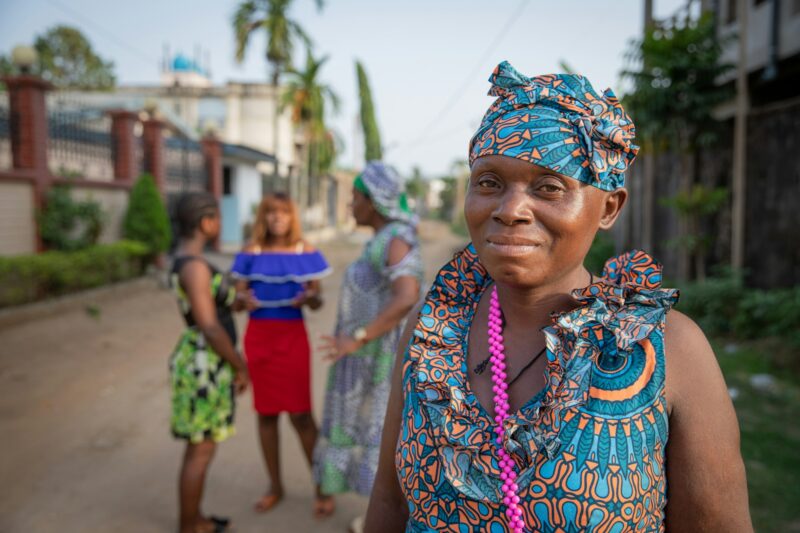
Impact On Society
Cultural diversity in Cameroon plays a vital role in shaping the society by celebrating unique traditions. Various ethnic groups contribute to the rich tapestry of indigenous languages and customs. This diversity fosters unity and understanding among communities, promoting tolerance and respect. It also encourages inclusivity and acceptance of different perspectives, leading to a peaceful coexistence. Embracing cultural differences enhances social harmony and strengthens the national identity of Cameroon.
Frequently Asked Questions For Cameroon’s Cultural Diversity: Exploring Ethnic Groups And Indigenous Languages
What Are The Major Ethnic Groups In Cameroon?
Cameroon is home to over 200 ethnic groups, with the major ones being the Bamileke, Fulani, and Tikar. Each group has its own unique cultural practices, traditions, and languages, contributing to the country’s rich diversity.
How Many Indigenous Languages Are Spoken In Cameroon?
Cameroon boasts approximately 230 indigenous languages, reflecting the country’s cultural richness and diversity. These languages play a vital role in shaping the identity and heritage of the various ethnic groups across the nation.
What Cultural Traditions Are Unique To Cameroon’s Ethnic Groups?
Cameroon’s ethnic groups hold diverse cultural traditions, including colorful festivals, intricate art forms, and traditional music and dance. Each group has its own distinct customs and rituals, enriching the nation’s cultural tapestry.
How Does Cameroon’s Cultural Diversity Impact The Country?
Cameroon’s cultural diversity contributes to a dynamic and vibrant society, fostering a deep sense of unity among its people. It serves as a testament to the nation’s ability to embrace and celebrate differences, promoting multicultural understanding and appreciation.
Conclusion
To truly grasp the essence of Cameroon’s cultural diversity, one must delve into the myriad ethnic groups and their indigenous languages. This exploration reveals a rich tapestry of traditions, customs, and ways of life that contribute to the country’s unique identity.
From the Fulani people of the North to the Beti people in the South, each ethnic group brings its own distinct language and customs, creating a vibrant mosaic that is distinctly Cameroonian. Understanding and celebrating this diversity is not just an academic exercise, but a way to foster unity and appreciation for the richness of humanity.
Let us embrace the beauty and significance of Cameroon’s cultural tapestry, cherishing the numerous ethnic groups and their invaluable contributions.